The US military now uses more solar power and renewable energy. This supports broader sustainability objectives. It also gives tactical benefits. The military is switching to clean energy sources like solar.
This reflects priorities beyond operations, like sustainability. Solar power provides advantages in the field. It also helps the military achieve climate goals.
Read on to learn how solar energy is changing defense operations. New programs and technologies drive this clean energy transition. They allow solar power to transform the Department of Defense.
For the US armed forces, expanding the use of renewable energy through collaboration with commercial solar installers serves both practical and ideological purposes.
Practically, solar and sustainable resources enhance mission efficiency and resilience. Renewables enable off-grid operations, reducing reliance on vulnerable fuel convoys. This also lowers long-term costs compared to fossil fuels.
Philosophically, the military seeks to set an example in addressing climate change. Expanding renewable energy demonstrates dedication to sustainability. This alignment with broader US objectives is evident.
The Department of Defense (DoD) now views renewables as vital to national security. Since 2009 it has increased alternative energy investments by over 500% to over $2.7 billion annually. The Army, Navy, Marines, Air Force, and Coast Guard all actively incorporate solar across operations.
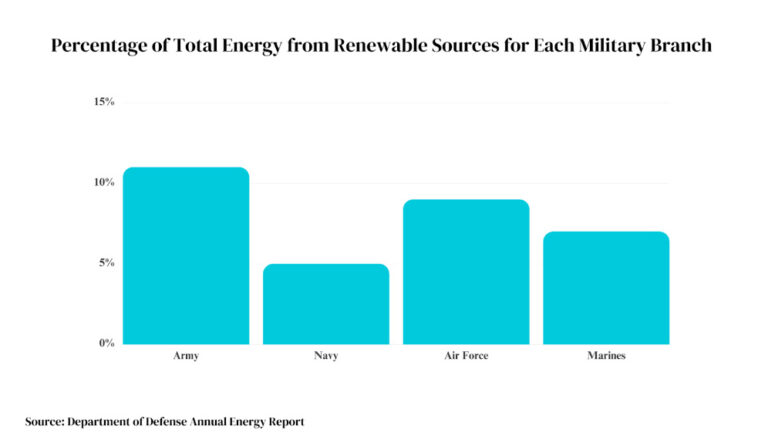
Data Source: Department of Defense Annual Energy Report
By embracing renewables, the military bolsters capabilities while catalyzing wider positive impacts.
For units in the field, portable solar power kits provide critical off-grid capabilities. These systems allow sustained operations in remote areas without relying on risky fuel convoys or local grid access. Solar advantages in expeditionary missions include:
Rugged portable solar panels are designed to withstand harsh environments. Mobile units can quickly transport and set up solar kits by vehicle, ship, or helicopter. Systems include suitcase-sized chargers for small patrols. They also feature trailer-based generators for powering forward operating bases.
Solar energy’s silent, renewable nature also provides stealth benefits in tactical situations. By reducing fuel requirements, solar-powered units have greater flexibility and security.
Across permanent installations, the armed forces rapidly deploy large-scale renewable energy projects. The DoD has over 130 operational renewable energy projects in the US and abroad.
On-site power generation from solar, wind, geothermal, and sustainable sources ensures bases can maintain critical functions. This resilience comes into play if the commercial grid goes down. It also provides cost savings and insulation from electricity market volatility.
Solar initiatives at US bases now deliver over 750 megawatts of capacity, including:
Meeting aggressive installation renewable targets brings significant financial benefits to the DoD. Simultaneously, it advances the agency’s net zero energy strategies.
Beyond supporting basic operations, solar power enables advanced military capabilities in several domains:
Space:
Off-grid solar energy powers remote satellite ground stations and high-altitude communications relay critical space infrastructure.
Air:
Solar aircraft utilize unlimited flight endurance for reconnaissance. Photovoltaic coatings embedded in planes supply onboard systems.
Land:
Silent watchtowers and sensors with integrated solar avoid detection while providing continual surveillance.
Sea:
Solar and wind systems provide fuel-free propulsion for unmanned vessels. They also recharge while aboard ships, enhancing sustainability.
Human:
Wearable solar fabrics and thin-film chargers keep individual operators powered on extended missions.
Solar-enabled innovations give warfighters expanded reach and flexibility across all environments.
Extreme weather is an increasing risk to military infrastructure and operations. Solar microgrids with battery storage give important resilience. They let mission-critical bases maintain power if severe events, cyber-attacks, or grid failures disrupt commercial electricity.
The Department of Defense prioritizes rapid islanding abilities at installations as a top priority. These include strategic missile defense, military mobilization, and special forces. Solar microgrids and intelligent load management are key to ensuring continuity of operations in any situation.
Cyber-secure microgrids also protect forward operating bases in conflict zones. They shield bases from external supply disruptions. By providing self-sufficient and resilient electricity, solar and storage systems sustain military capabilities when risks are highest.
Solar microgrids allow bases to isolate quickly and operate independently. Battery storage enables essential loads to stay online during disruptions. Together, they provide crucial resilience against extreme weather and attacks. This maintains mission-critical operations.
Solar power goes beyond facilities and equipment. It keeps individual troops connected and effective during distributed operations. Portable solar solutions issued to soldiers, sailors, marines, and airmen include:
Distributing solar capabilities across the unit allows agile, resilient missions. The military maximizes adoption through wireless power-sharing between networked troops. Harnessing the sun keeps warfighters continuously linked to vital communications, sensors, and information.
DoD serves as an early adopter and developer of cutting-edge renewable technologies. It partners with private industry, labs, and academia to incubate emerging capabilities.
Areas of solar-related research include:
The military fast-tracks next-gen renewable solutions into the field through demonstrations and partnerships. This drives wider commercialization and national energy innovation.
Many military solar projects make more energy than bases need, especially if built for expansion. The Department of Defense reuses these renewable power surpluses through community partnerships.
Excess clean energy goes to local civilian grids, improving regional resilience. Solar microgrids connect military networks to nearby towns, businesses, and public services. This enhances collective readiness and resilience.
Solar surpluses also help the armed forces build goodwill through energy assistance programs. These include:
Leveraging extra solar capacity strengthens civil-military cooperation. It also progresses the military’s goals to deploy capabilities benefiting society overall.
Solar energy powers soldiers, bases, and vehicles. This transforms 21st-century defense strategy. Renewable technologies improve military resilience, effectiveness, and efficiency. They also give strategic advantages.
The military’s use of solar power reflects a broader imperative. America must lead in fighting climate change. It can do this through clean energy innovation. Solar helps the armed forces confront climate issues. It makes them a leader in sustainability. The military’s transition to solar energy drives tactical and climate-related advancements.
How much does the US military spend on energy annually?
The DoD spends around $4 billion per year on facility energy and over $10 billion on operational fuels. Reducing these costs through renewables provides major budgetary savings.
What percentage of military energy use comes from renewable sources?
As of 2020, roughly 6% of the total DoD energy consumption was derived from renewable sources. The military aims to achieve at least 25% renewable energy consumption by 2025 through extensive solar and other sustainable projects.
Which military branch uses the most solar power?
Currently, the US Army is the top military solar user, followed by the Air Force, Navy, and Marines. However, all branches are expanding renewable adoption to improve capabilities.
How does solar energy provide tactical advantages?
Solar allows silent watchtowers, off-grid patrols, and reduced convoys to avoid detection. It also enables unmanned systems with unlimited endurance for ISR and other missions.
Do solar panels work as effectively on cloudy days?
Solar output decreases on cloudy days but still produces usable energy through diffuse light. Battery storage mitigates the effects of intermittent sunshine. Panel efficiency is continually improving.